
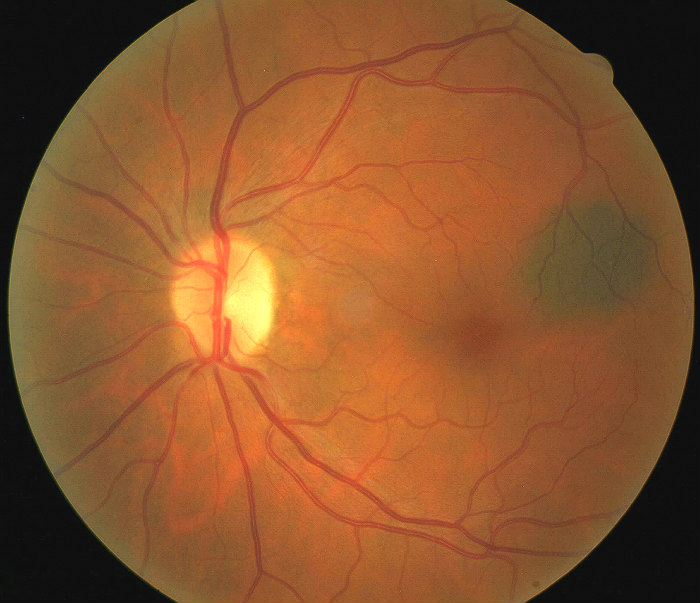
Up to 50% of patients with pathologic myopia are reported to have a staphyloma.

Patients with pathologic myopia are at increased risk for posterior staphylomas.

Up to 9% of Asian and 2% of White population in the United States have pathologic myopia, which increases their likelihood of having concurrent posterior staphyloma. The progression of posterior staphyloma may not stop at any specific age, unlike the moderate myopia cases which usually stabilize at around 18-21 years of age. Posterior staphyloma, at the posterior pole, behind the equator.Equatorial, at the equator of the globe.Ciliary, involving the ciliary body, just behind the limbus.Anterior, involving cornea and surrounding sclera.According to the location, staphyloma may be classified as Staphylus (Greek) means cluster of grapes and staphyloma gets its name from this. In staphyloma the wall of the globe (cornea or sclera) are ectatic/thin and bulging with uveal tissue in it giving it a pigmented color. Types of staphyloma according to location Staphylomas that occur anteriorly are often acquired, while those that are posterior are congenital or due to extreme myopia. However, it can be present in non-myopic eyes, often acquired secondarily due to infection or trauma. Posterior staphyloma is considered a hallmark of pathologic myopia and are among one of the major causes of developing maculopathy. 2.5 Differential Diagnosis Ī staphyloma is a circumscribed outpouching of the wall of the globe.1.4 Risk Factors & Associated Conditions.1.2 Types of staphyloma according to location.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
